


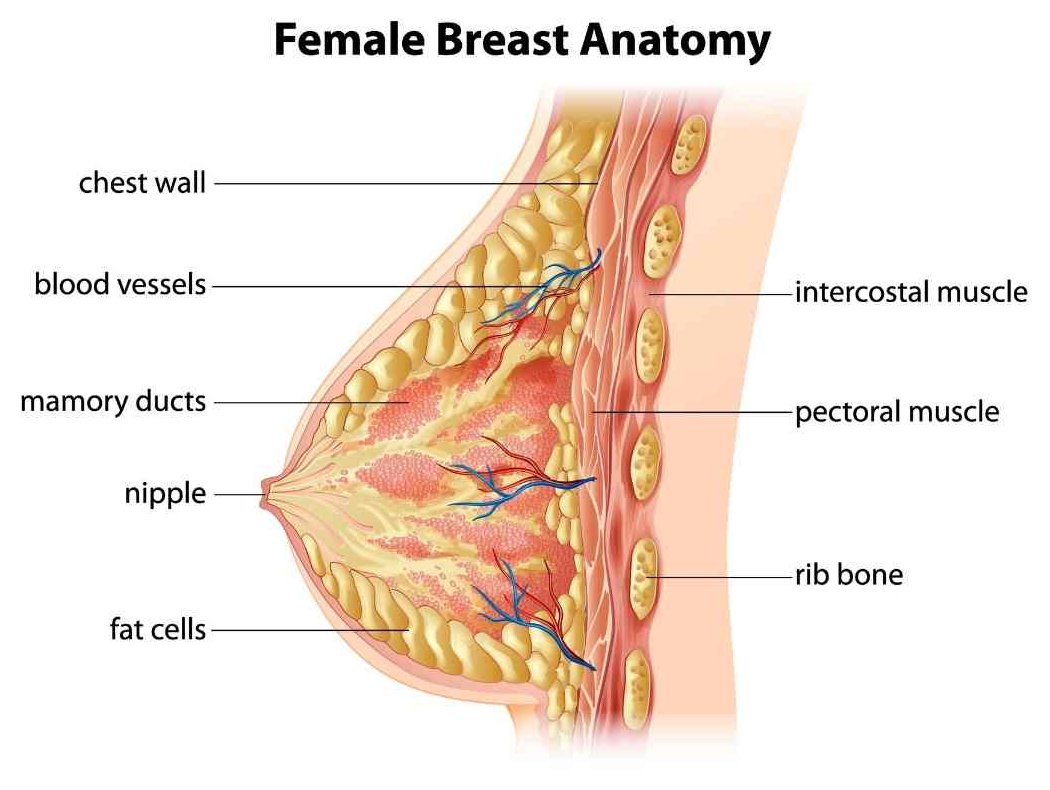
Anatomy
The breast is the tissue overlying the chest (pectoral) muscles. Women’s breasts are made of specialized tissue that produces milk (glandular tissue) as well as fatty tissue. The amount of fat determines the size of the breast.
The milk-producing part of the breast is organized into 15 to 20 sections, called lobes. Within each lobe are smaller structures, called lobules, where milk is produced. The milk travels through a network of tiny tubes called ducts. The ducts connect and come together into larger ducts, which eventually exit the skin in the nipple. The dark area of skin surrounding the nipple is called the areola. 1
Genetics + breast shapes
Breast size is a highly heritable trait. A twin study previously estimated the heritability of bra cup size to be 56%. Several genome-wide association studies have also identified common genetic variants associated with breast size. 2
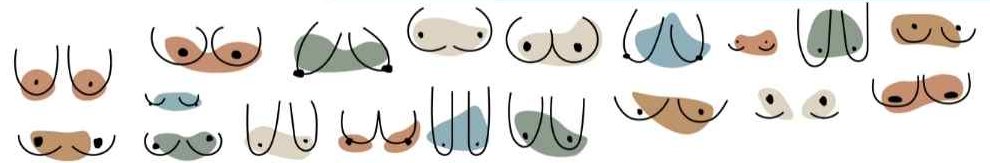
Breast shapes:
Asymmetric
This refers to sets of boobs where one is larger (or smaller) than the other.
Athletic
These breasts are wider, more muscular-looking, and have less tissue.
East West
If your nipples point in opposite directions outward, you probably have east west breasts.
Relaxed
For the relaxed type, your boobs typically hang downwards and have lax tissue.
Bell shape
Bell shape breasts are thinner at the top and fuller at the bottom.
Slender
Doesn’t necessarily mean that you wear a smaller cup size. Your boobs are on the thinner side.
Side set
Your boobs can be called side set if you have a little space between your breasts.
Round
Round boobs are the type that are fully circular, and equal at the top and bottom of the breasts.
Tear drop
Similar to round breasts, the tear drop shape is circular, but your boobs are a little less full at the top. 3
Asymmetric breasts
No one has a perfectly symmetrical body. So it’s not surprising that the left and right breasts can vary in size, shape, volume, and location. In some people, the difference isn’t striking, whereas, in others, one breast can be a full cup size bigger than the other. Usually, this is normal, especially in adolescent girls whose bodies are still developing. 4 It’s not clear why this happens. One explanation is that girls may have more breast tissue cells on one side. The cells may be more sensitive to the hormone estrogen, which causes breast tissue cells to grow. 5
Impacts on breast sizes

Body positive influencer

@clara_dao
Clara Dao she/her/hers
Digital Creator
HERE TO REMIND U TO LOVE UR BODY
I enjoy making body positivity videos & post silly pictures of myself sometimes

Information / Text Sources
1) https://www.webmd.com/women/picture-of-the-breasts
2) https://knix.com/blogs/resources/is-breast-size-hereditary
3) https://www.seventeen.com/health/sex-health/g23725507/different-boob-types-shapes/?slide=9
4) https://flo.health/menstrual-cycle/teens/your-body/breast-shapes-and-sizes
5) https://www.verywellhealth.com/one-breast-bigger-than-other-3969225
6) https://www.self.com/story/6-things-that-can-actually-impact-your-breast-size
